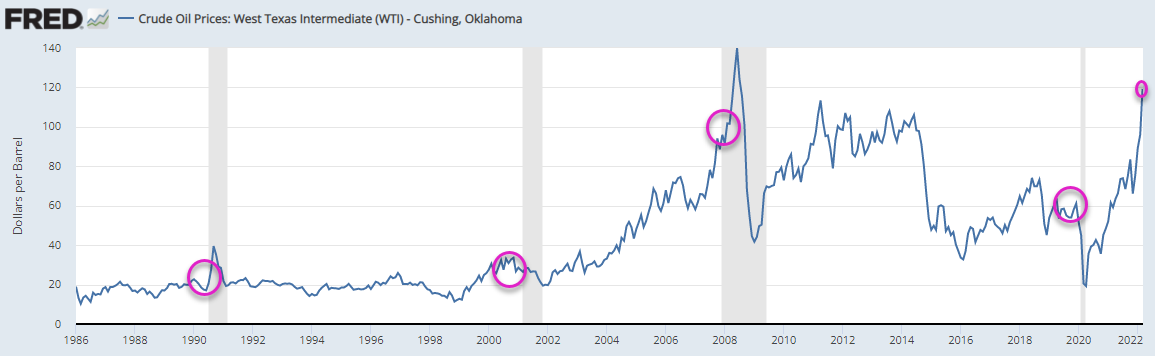
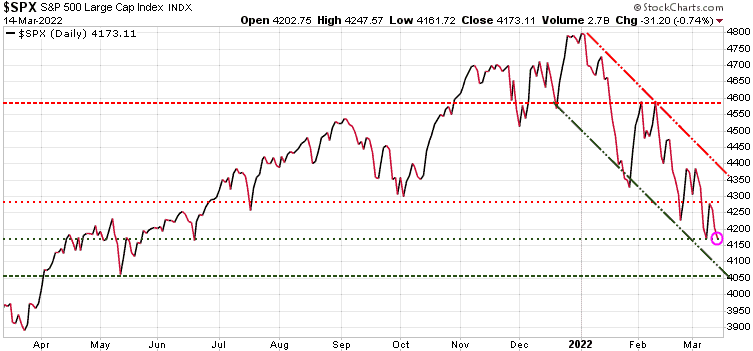
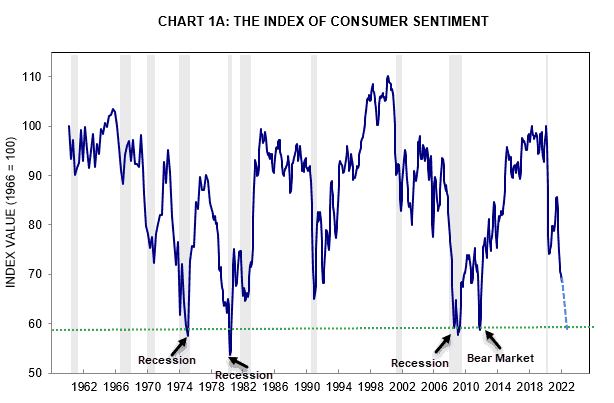
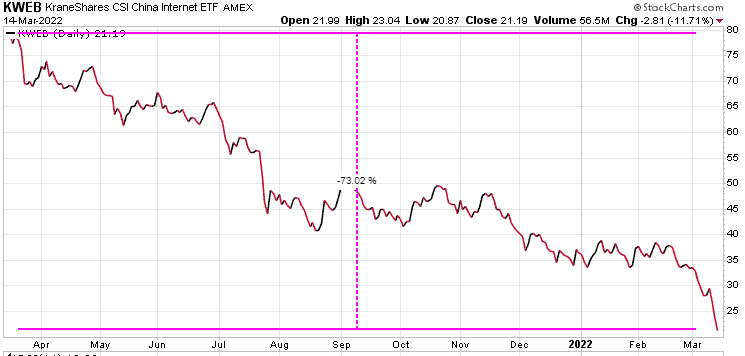
The Industrial Revolution took place in the last century, and in this century it is being mirrored by the Technology Revolution, in the sense that jobs are changing, disappearing, or being automated. Artificial Intelligence (AI) can incorporate machine learning (ML) to analyze a job and “think” of the best or a better way to get it done, and also resolve problems along the way. However, there are some well defined repetitive jobs that can be automated with simpler programming than AI requires, and this is the expanding world of Robotic Processing Automation (RPA).
There are tasks in many industries that can benefit from using RPA. Tasks that are very repetitive, well defined, and/or tedious for humans, can be handed over to RPA bots. These bots may need a little human supervision to ensure problem free execution, but for the most part RPA can motor along with no help needed at all. Here are some examples of where RPA is being put to use today:
Financial Services: Opening accounts, high volume data entry, inquiry processing, customer research
Healthcare: Prescription management, insurance claim processing, payment cycles, patient records
Retail: Customer relationship management, order management, fraud detection, warehouse management
Insurance: Claims processing, policy management, regulatory compliance, underwriting tasks, form filling
In order for RPA to work well it does need some important design considerations, such as low-coding capabilities to facilitate fast development of automation scripts, effective integration with enterprise applications, the ability to administer and orchestrate tasks securely, and the ability to be monitored. Automation technology, like RPA, can also access information through legacy systems, integrating well with other applications through front-end integrations. This allows the automation platform to behave similarly to a human worker, performing routine tasks, such as logging in and copying and pasting from one system to another. While back-end connections to databases and enterprise web services also assist in automation, RPA’s real value is in its quick and simple front-end integrations.
The are several strong benefits to using RPA, such as:
- Cost savings, as many high-volume tasks are handled by RPA and staff can be re-assigned to higher priority work that actually requires human input. Efficiency and ROI are improved.
- Accuracy and compliance are improved as RPA reduces human error and provides a good audit trail
- Less coding, as low-code development can be much faster and cheaper
- Keep current systems, as RPA works on the presentation layer with no need for complicated system integrations.
- Staff morale, as RPA can relieve high-volume staff workloads and thus allow staff to focus on strategic decision making, resulting in enhanced job satisfaction.
There are some challenges that RPA can struggle with, such as operating in an environment where regulations and/or processes change frequently, making it difficult to scale up to enterprise-wide implementation. While RPA can reduce the need for certain job roles, it can also drive growth in new jobs that tackle more complex tasks, enabling staff to focus on higher-level strategy and creative problem-solving. Organizations will need to promote a culture of learning and innovation. The adaptability of a workforce will be important for successful outcomes in automation and digital transformation projects. By educating staff and investing in training programs, staff can be prepared for ongoing shifts in priorities. Training and innovation can pave the way for RPA.
The goal of TREND DISRUPTORS is to discover and monitor technical developments that have the potential to DISRUPT a market sector. We look for the best ideas, so that we can generate actionable investment recommendations for subscribers. As a general rule, our recommendations are speculative, and we advise caution, discretion, and thorough research. We strive to identify investment opportunities that can lead to success for the well-informed investor.
Stay tuned!